AEtest (Automation Easy Testing) offers a simple and straightforward way for users to define, execute and debug testcases and testscripts. AEtest is available as a standard component (aetest) in pyATS in an effort to standardize the definition and execution of testcases & testscripts.
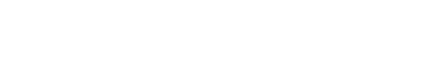
AEtest testscript structure is very modular and straightforward. Each testscript is split into three major container sections which are then further broken down into smaller, method sections. These three containers are Common Setup, Testcase(s), and Common Cleanup. Throughout the steps in this section of the lab, you will examine each of these.
In VSCode, using the code keyword in the Terminal window, open a new file for creating a Python pyATS AEtest script:
touch /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/pyats_aetest.py
code-server -r /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/pyats_aetest.py
Like you did in the Python requests section for NX-API, you need to import some modules. In this case we need to import pyATS aetest module and the load module from pyATS Genie.
The logging import is pretty self-explanatory; for logging. And finally, the unicon import is for catching a ConnectionError in subsequent parts of your code.
from pyats import aetest
from genie.testbed import load
import logging
import yaml
import os
from unicon.core.errors import ConnectionError
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
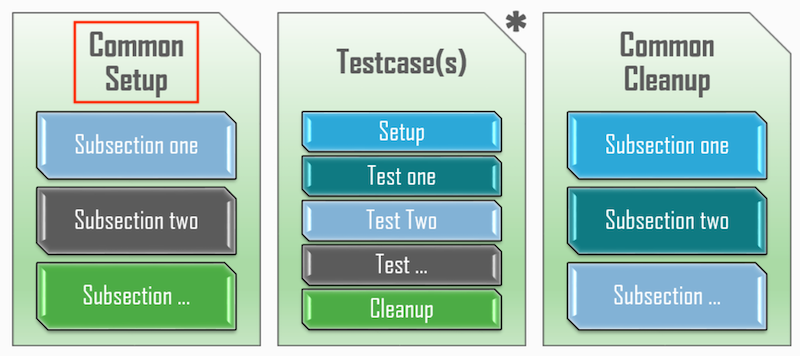
CommonSetup is an optional section within each testscript, defined by inheriting the aetest.CommonSetup class, and declaring one or more Subsections inside. CommonSetup always runs first, and is where all the common configurations, prerequisites and initializations shared between the script's testcases should be performed.
This includes but is not limited to the following:
class CommonSetup(aetest.CommonSetup):
@aetest.subsection
def connect(self, testbed):
"""
establishes connection to all your testbed devices.
"""
# make sure testbed is provided
assert testbed, "Testbed is not provided!"
if len(testbed.devices) == 0:
self.failed('{testbed} is empty'.format(testbed=str(testbed)))
else:
# connect to all testbed devices
# By default ANY error in the CommonSetup will fail the entire test run
# Here we catch common exceptions if a device is unavailable to allow test to continue
try:
for device in testbed:
device.connect(via='rest')
except (TimeoutError, ConnectionError):
logger.error("Unable to connect to all devices")
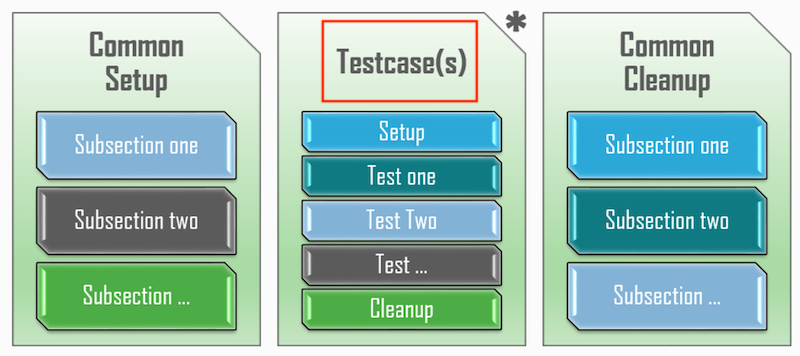
Testcase is a collection of smaller tests. Testcases are the actual tests to be performed against the device under test. Each testcase may have its own Setup Section and Cleanup Section, and an arbitrary number of smaller Test Sections.
Each Testcase is defined by inheriting aetest.Testcase class, and defining one or more Test Sections inside. Optionally, each Testcase may also have a single Setup Section and a single Cleanup Section. Testcases run in the order as they are defined in the testscript.
class verify_connected(aetest.Testcase):
"""verify_connected
Ensure successful connection to all devices in testbed.
"""
@aetest.test
def test(self, testbed, steps):
# Loop over every device in the testbed
for device_name, device in testbed.devices.items():
with steps.start(
f"Test Connection Status of {device_name}", continue_=True
) as step:
# Test "connected" status
if device.connected:
logger.info(f"{device_name} connected status: {device.connected}")
else:
logger.error(f"{device_name} connected status: {device.connected}")
step.failed()
error_occurred = True
class verify_ospf_process_id(aetest.Testcase):
"""verify_ospf_process_id
"""
@aetest.test
def test(self, testbed, steps):
command = 'show ip ospf neighbors'
# Loop over every device in the testbed
for device_name, device in testbed.devices.items():
with steps.start(
f"Verify OSPF Process ID is UNDERLAY on {device_name}", continue_=True
) as step:
output = device.api.nxapi_method_nxapi_cli('send', command, message_format='json', command_type='cli_show', alias='rest').json()
ospf_process_id = output['ins_api']['outputs']['output']['body']['TABLE_ctx']['ROW_ctx']['ptag']
if ospf_process_id == 'UNDERLAY':
logger.info(f"{device_name} OSPF Process ID: {ospf_process_id}")
else:
logger.error(f"{device_name} OSPF Process ID: {ospf_process_id}")
step.failed()
class verify_ospf_neighbor_count(aetest.Testcase):
"""verify_ospf_neighbor_count
"""
@aetest.test
def test(self, testbed, host_vars, steps):
command = 'show ip ospf neighbors'
# Loop over every device in the testbed
for device_name, device in testbed.devices.items():
with steps.start(
f"Verify OSPF Neighbors on {device_name}", continue_=True
) as step:
file_path = os.path.join(host_vars, f"{device_name}.yml")
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
vars_data = yaml.safe_load(f)
interfaces = vars_data.get('layer3_physical_interfaces', [])
ospf_count = sum(1 for iface in interfaces if 'ospf' in iface)
output = device.api.nxapi_method_nxapi_cli('send', command, message_format='json', command_type='cli_show', alias='rest').json()
ospf_nbr_count = output['ins_api']['outputs']['output']['body']['TABLE_ctx']['ROW_ctx']['nbrcount']
if ospf_nbr_count == ospf_count:
logger.info(f"{device_name} OSPF Neighbor Count: {ospf_nbr_count}")
else:
logger.error(f"{device_name} OSPF Neighbor Count: {ospf_nbr_count}")
step.failed()
class verify_ospf_neighbor_state(aetest.Testcase):
"""verify_ospf_neighbor_state
"""
@aetest.test
def test(self, testbed, steps):
command = 'show ip ospf neighbors'
# Loop over every device in the testbed
for device_name, device in testbed.devices.items():
with steps.start(
f"Verify OSPF Neighbors on {device_name}", continue_=True
) as step:
output = device.api.nxapi_method_nxapi_cli('send', command, message_format='json', command_type='cli_show', alias='rest').json()
ospf_nbrs = output['ins_api']['outputs']['output']['body']['TABLE_ctx']['ROW_ctx']['TABLE_nbr']['ROW_nbr']
if isinstance(ospf_nbrs, list):
for ospf_nbr in ospf_nbrs:
if ospf_nbr['state'] == 'FULL':
logger.info(f"{device_name} OSPF Neighbor State: {ospf_nbr['state']}")
else:
logger.error(f"{device_name} OSPF Neighbor State: {ospf_nbr['state']}")
step.failed()
else:
if ospf_nbr['state'] == 'FULL':
logger.info(f"{device_name} OSPF Neighbor State: {ospf_nbr['state']}")
else:
logger.error(f"{device_name} OSPF Neighbor State: {ospf_nbr['state']}")
step.failed()
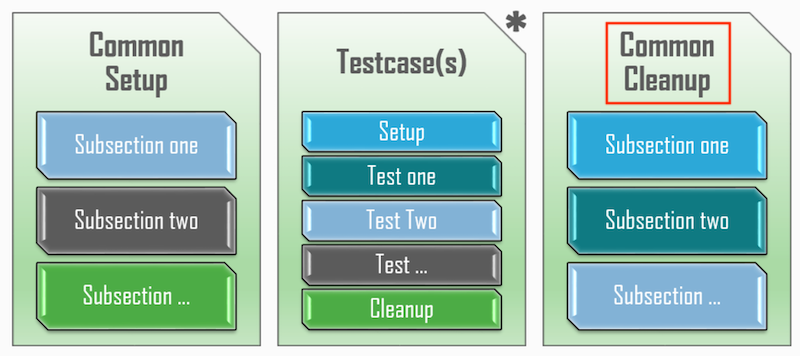
CommonCleanup is the last section within each testscript. Any configurations, initializations and environment changes that occurred during this script run should be cleaned up or removed here. Eg, the testbed/environment should be returned to the same state as it was before the script run. This includes but is not limited to:
class CommonCleanup(aetest.CommonCleanup):
@aetest.subsection
def disconnect_from_devices(self, testbed):
for device in testbed:
# Only disconnect if we are connected to the device
if device.is_connected() == True:
device.disconnect()
This main function should look similar in comparison to the Python NX-API section, albeit, a bit shorter. The logging level is set first. Next, the AEtest main method is invoked to kickoff the script sections you defined.
if __name__ == '__main__':
# set logger level
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
aetest.main()
Executing this script by calling the aetest.main() function is considered a standalone execution. It can be done now, however additional functionality is gained if run using the EasyPy Execution method as seen in the next step.
In VSCode, using the code keyword in the Terminal window, open a new file for creating a Python pyATS EasyPy script:
touch /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/pyats_easypy.py
code-server -r /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/pyats_easypy.py
Add the small snippet of code below into the pyats_easypy.py file that sets the path lookup for the pyats_aetest.py script file:
import os
import argparse
from pyats.easypy import run
# script path from this location
SCRIPT_PATH = os.path.dirname(__file__)
def main():
'''job file entrypoint'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--host_vars', type=str, default=None)
args, _ = parser.parse_known_args()
# run script
run(testscript=os.path.join(SCRIPT_PATH, 'pyats_aetest.py'), host_vars=args.host_vars)
Scripts executed with Easypy - Runtime Environment are called EasyPy Execution. In this mode, all environment handling and control is set by the EasyPy launcher. For example, the following features are available:
Execute your AEtest script using EasyPy via the pyATS command line run command, pyats run job to test and verify the expected configuration and state of OSPF.
Notice the --testbed-file option that makes use of the testbed file you defined previously for how to connect to your devices.
pyats run job pyats_easypy.py --testbed-file staging-testbed.yaml --host_vars ${PWD}/../ansible-nxos/host_vars/ --archive-dir=${PWD}/results --no-archive-subdir --no-mail
You will have to scroll up on the Terminal some, but your test script execution should look like the below. Notice there is a summary, Task Result Summary, for each section, i.e. the sections you built out above in your code. Also notice the detailed results, Task Result Details for each testcase run against each device.
2026-02-09T20:40:33: %EASYPY-INFO: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2026-02-09T20:40:33: %EASYPY-INFO: Job finished. Wrapping up... 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Creating archive file: /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/results/pyats_easypy_2026Feb09_20_39_29_718915.zip 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | Easypy Report | 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: pyATS Instance : /home/pod01/.pyenv/versions/3.11.14/envs/nxapilab 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Python Version : cpython-3.11.14 (64bit) 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: CLI Arguments : /home/pod01/.pyenv/versions/nxapilab/bin/pyats run job pyats_easypy.py --testbed-file staging-testbed.yaml --host_vars /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/../ansible-nxos/host_vars/ --archive-dir=/home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/results --no-archive-subdir --no-mail 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: User : pod01 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Host Server : ubuntu-code-server-template 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Host OS Version : Ubuntu 22.04 jammy (x86_64) 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Job Information 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Name : pyats_easypy 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Result : PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Start time : 2026-02-09 20:39:39.546174+00:00 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Stop time : 2026-02-09 20:40:33.716103+00:00 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Elapsed time : 0:00:55 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Archive : /home/pod01/workspace/nxapilab/tests/results/pyats_easypy_2026Feb09_20_39_29_718915.zip 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Total Tasks : 1 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Overall Stats 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Passed : 6 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Passx : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Failed : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Aborted : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Blocked : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Skipped : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Errored : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: TOTAL : 6 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Success Rate : 100.00 % 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Section Stats 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Passed : 6 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Passx : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Failed : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Aborted : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Blocked : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Skipped : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Errored : 0 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: TOTAL : 6 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Section Success Rate : 100.00 % 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | Task Result Summary | 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest.common_setup PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest.verify_connected PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest.verify_ospf_process_id PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest.verify_ospf_neighbor_count PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest.verify_ospf_neighbor_state PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest.common_cleanup PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | Task Result Details | 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Task-1: pyats_aetest PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: |-- common_setup PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- connect PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: |-- verify_connected PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- test PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 1: Test Connection Status of staging-spine1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 2: Test Connection Status of staging-spine2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 3: Test Connection Status of staging-leaf1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 4: Test Connection Status of staging-leaf2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- STEP 5: Test Connection Status of staging-leaf3 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: |-- verify_ospf_process_id PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- test PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 1: Verify OSPF Process is UNDERLAY on staging-spine1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 2: Verify OSPF Process is UNDERLAY on staging-spine2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 3: Verify OSPF Process is UNDERLAY on staging-leaf1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 4: Verify OSPF Process is UNDERLAY on staging-leaf2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- STEP 5: Verify OSPF Process is UNDERLAY on staging-leaf3 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: |-- verify_ospf_neighbor_count PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- test PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 1: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-spine1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 2: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-spine2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 3: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-leaf1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 4: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-leaf2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- STEP 5: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-leaf3 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: |-- verify_ospf_neighbor_state PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- test PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 1: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-spine1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 2: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-spine2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 3: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-leaf1 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | |-- STEP 4: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-leaf2 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: | `-- STEP 5: Verify OSPF Neighbors on staging-leaf3 PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: `-- common_cleanup PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: `-- disconnect_from_devices PASSED 2026-02-09T20:40:34: %EASYPY-INFO: Done!
Navigate back to your VSCode application.
Once completed, continue to the next section to examine pyATS testing using the RobotFramework.