Another transport mechanism to push configuration changes or read network device configuration that uses YANG data models is the HTTP-based Representational State Transfer Configuration Protocol or RESTCONF. Like NETCONF, RESTCONF uses structured data for YANG models to provide REST-like APIs. The structured data, again like NETCONF, can be represented as XML, but also allows the use of JSON.
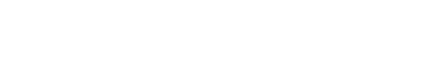
Similar to NETCONF, RESTCONF uses standard HTTP operations.
RESTCONF allows us to use standard GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE methods in REST to manipulate and retrieve data
backed by YANG models. Let's take a look at how operations on RESTCONF compare to NETCONF.
RESTCONF has been in discussion among major players since 2014, however the RFC was just ratified for publication as recently as January 2017. Please read the RFC's introduction as it provides a great overview.
1. Introduction
There is a need for standard mechanisms to allow Web applications to
access the configuration data, state data, data-model-specific Remote
Procedure Call (RPC) operations, and event notifications within a
networking device, in a modular and extensible manner.
This document defines a protocol based on HTTP [RFC7230] called
"RESTCONF", for configuring data defined in YANG version 1 [RFC6020]
or YANG version 1.1 [RFC7950], using the datastore concepts defined
in the Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) [RFC6241].
NETCONF defines configuration datastores and a set of Create, Read,
Update, Delete (CRUD) operations that can be used to access these
datastores. NETCONF also defines a protocol for invoking these
operations. The YANG language defines the syntax and semantics of
datastore content, configuration, state data, RPC operations, and
event notifications.
RESTCONF uses HTTP methods to provide CRUD operations on a conceptual
datastore containing YANG-defined data, which is compatible with a
server that implements NETCONF datastores.
If a RESTCONF server is co-located with a NETCONF server, then there
are protocol interactions with the NETCONF protocol; these
interactions are described in Section 1.4. The RESTCONF server MAY
provide access to specific datastores using operation resources, as
described in Section 3.6. The RESTCONF protocol does not specify any
mandatory operation resources. The semantics of each operation
resource determine if and how datastores are accessed.
Configuration data and state data are exposed as resources that can
be retrieved with the GET method. Resources representing
configuration data can be modified with the DELETE, PATCH, POST, and
PUT methods. Data is encoded with either XML [W3C.REC-xml-20081126]
or JSON [RFC7159].
Data-model-specific RPC operations defined with the YANG "rpc" or
"action" statements can be invoked with the POST method. Data-model-
specific event notifications defined with the YANG "notification"
statement can be accessed.
Navigate here for the full RFC if you are interested in learning more.
When working with YANG models over RESTCONF, a key concept is to understand how the URL specified maps to the underlying YANG model being accessed.
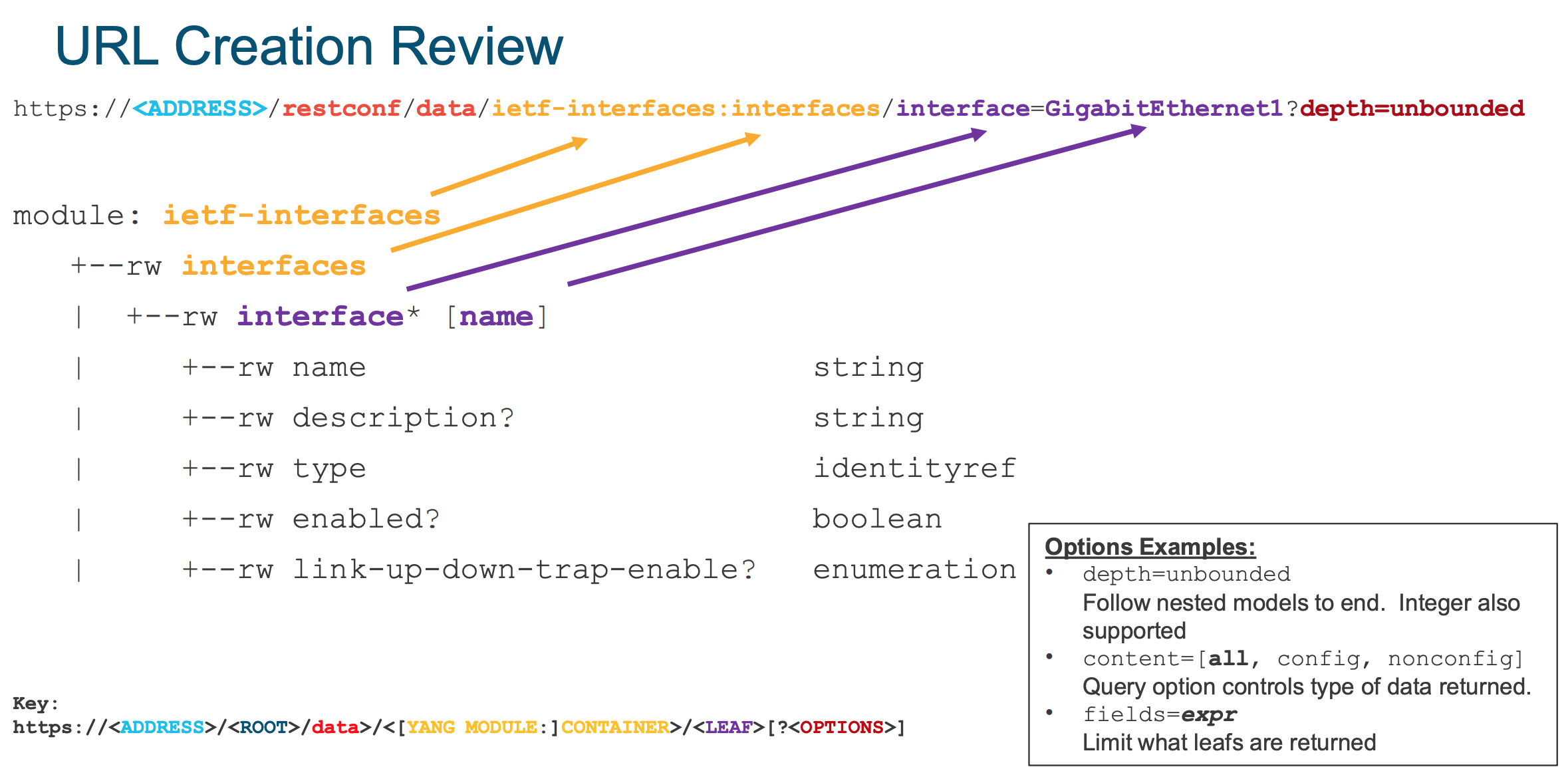
Later in this section of the lab you will use the concepts presented in this visual to apply configuration using YANG models.